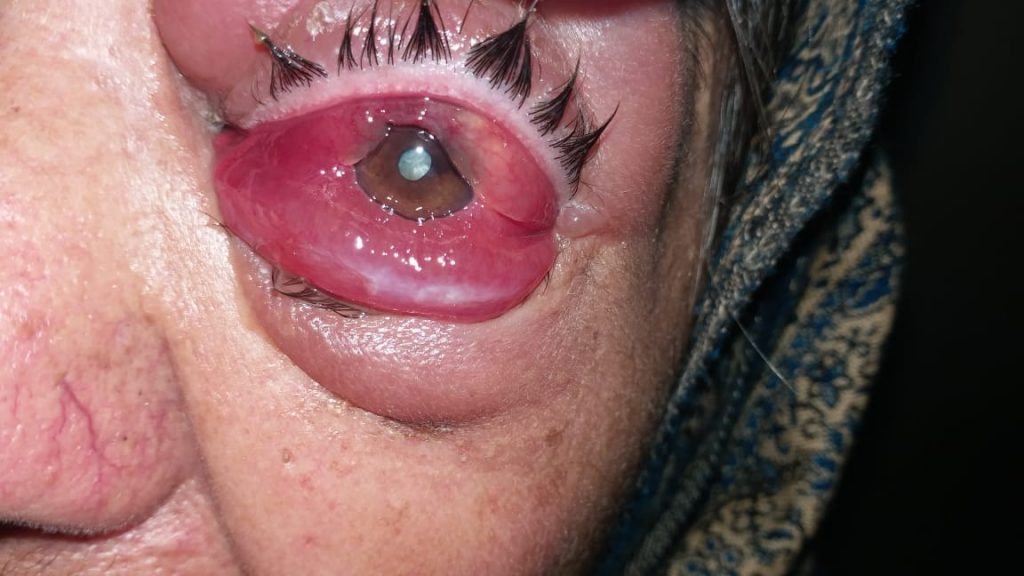
Orbital pseudotumor or idiopathic orbital inflammatory syndrome (IOIS) is a rare inflammatory condition of the eye without a known cause.
Diagnosis …
It is often a diagnosis of exclusion. Diagnosis to consider in a patient presenting with eye swelling and redness include:
- Orbital cellulitis
- Orbital neoplasms
- Systemic disorders like Wegener’s Granulomatosis, and
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis
- Tolosa Hunt syndrome
The true incidence of the disease is not known since a uniform definition and a universally accepted definition is lacking.
However, the diagnosis requires the exclusion of other orbital diseases like infections and systemic disorders and may require biopsy.
Patients usually present with an abrupt onset of unilateral or bilateral eye swelling with pain, redness, restricted eye movements, impaired or double vision with nausea and headache.
MR findings in patients with orbital pseudotumor
Magnetic resonance imaging may reveal symmetrical involvement of both the optic nerves, lacrimal glands, orbital fats, muscles.
In contrast to Graves ophthalmopathy in which invovlement of the muscles reveal a spindle shaped configuration with normal tendons, orbital pseudotumor is characterized by diffuse hypertrophy of the muscles and tendons leading to a tubular pattern.
There is diffuse hypertrophy and enlargement of the lacrimal glands, perineural optic sheath complex, diffusely enlarged tendons and muscles of the orbit with fixation impairing mobility of the eye and proptosis.
Histopathlogical findings …
Biopsy findings may include:
- focal or diffuse mononuclear and phagocytic infiltrate in the interstitium associated with fibrosis,
- Granuloma formation, and
- Fat infiltration.
The most important aspect of treating orbital pseudotumor is exluding other differential diagnosis and prompt initiation of steroids. Patients respond rapidly to steroids, however, treatment may be prolonged to avoid relapses.
Treatment of orbital pseudotumor
Patients who fail to respond to steroids may be advised local radiotherapy, especially in severe cases. Methotrexate, cyclosporin, and cyclophosphamide have not been studied but may be used as steroid-sparing agents. Immunomodulators may especially benefit patients who have a relapse.
Read More ….
Bulging eyes – Graves ophthalmopathy