Sexual disorders in men relate to any of the following three components: Diminished Libido, Erectile dysfunction, and Ejaculatory dysfunction.
As age advances, sexual dysfunction becomes more common. Up to 40% of men above 40 years of age notice a decline in one or more of the following domains of sexual function:
Sexual intercourse, erection frequency, sexual desire, satisfaction, and orgasm.

Decreased libido:
Decreased libido is estimated to affect up to 15% of the patients. Few of the important causes of a reduced libido include:
- Medications (SSRIs, anti-androgens, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, opioid analgesics)
- Alcoholism
- Depression
- Fatigue
- Hypoactive sexual disorder
- Recreational drugs
- Relationship problems
- Other sexual dysfunction (fear of humiliation)
- Sexual aversion disorder
- Systemic illness
- Testosterone deficiency

Reduced libido may also be secondary to erectile dysfunction. Therefore, treating erectile dysfunction may treat reduced libido to some extent.
In addition, all the causes of reduced libido are potentially treatable. A proper medical history, examination, and investigations are important to treat the disorder.
Erectile dysfunction – a common sexual disorder in men
Erectile dysfunction is the most common sexual problem. It affects 15 to 35% of patients especially above 40 years of age.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is defined as the consistent or recurrent inability to acquire or sustain an erection of sufficient rigidity and duration for sexual intercourse.

Risk factors for erectile dysfunction include obesity, smoking, watching television and comorbid medical conditions like diabetes. On the contrary, exercise has been associated with a low risk of erectile dysfunction.
A reduction in weight and increasing physical activity improves erectile dysfunction in about a third of patients.
Similarly, in one study, it was found that men who had less frequent intercourse (less than once per week) developed erectile dysfunction at twice the rate as men who reported intercourse more than once per week.
Patients with comorbid conditions like Diabetes, the presence of risk factors for coronary artery disease ( smoking, obesity, and dyslipidemia), medication use and hypertension were also more likely to develop erectile dysfunction.
Other conditions associated with erectile dysfunction include systemic sclerosis (scleroderma), Peyronie’s disease, and prostate cancer treatment (eg, brachytherapy, prostatectomy).

Erectile dysfunction – Role of Drugs
Up to 25% of the patients with erectile dysfunction have it because of the side effect of a drug. The following is a list of the commonly prescribed drug causing problems in erection.
- Antidepressants – Most antidepressants are associated with ED, but in particular, the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Spironolactone
- Sympathetic blockers such as clonidine, guanethidine, or methyldopa
- Thiazide diuretics
- Ketoconazole
- Cimetidine but apparently not ranitidine or famotidine
Although erectile dysfunction is frequently associated with the use of beta blockers, studies have not shown any such adverse effects. However, thiazide diuretics have a significant association with erectile dysfunction.
Alpha blockers, on the other hand, were found to improve erectile dysfunction in hypertensive patients.
Common over-the-counter products contain chemicals like nicotine and alcohol that have a disruptive effect on male sexual function.

Although some recreational drugs, such as cocaine and heroin, can initially stimulate libido and sexual arousal, they ultimately exert a negative impact on the ability to acquire and sustain erectile function.
Judicious substitution of an equally effective but less sexually noxious prescription antihypertensive drug, H2 antagonist, or antidepressant, as well as recreational drug abstinence, may be sufficient to restore sexual function.
Psychosocial factors:
Depression, stress, or the drugs used to treat depression can result in Erectile Dysfunction.
Neurological:
Neurologic diseases like stroke, back injury, dementia, and multiple sclerosis can cause ED. Other than that pelvic trauma and prostate surgery may also cause ED.

Bicycling:
Bicycling and Horse riding are less common but controversial causes of ED. This association has been made because these two sports are associated with prolonged pressure on nerves and blood vessels supplying the penile tissue.
Endocrine causes of erectile dysfunction:
Testosterone is the main hormone responsible for all the components of a male sexual activity i.e. libido, erection, sperm production, and ejaculation. Treatment of ED with testosterone and especially testosterone plus PDE I in patients with low testosterone can lead to an improvement in ED.
The cut-off testosterone levels associated with ED in most studies has been found to be less than 225 ng/dl.
Other endocrine disorders associated with ED include high prolactin levels, thyroid disorders, and high cortisol levels.
In addition, ED is found in the majority of type 2 DM patients. Most of these patients are deficient in androgens. Other factors like neuropathy and vasculopathy also play their role.
Ejaculatory disorders in men:

Ejaculatory disorders are a heterogeneous group of disorders that include premature, delayed, and retrograde ejaculation, and anorgasmia.
Premature ejaculation (PE)
Premature ejaculation is characterized by early or brief ejaculation (usually less than one minute) with loss of control and associated psychological distress in the patient or the partner.
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) applies a cut-off of 15 seconds from the beginning of sexual intercourse
Most of the patients with premature ejaculation also have some degree of erectile dysfunction as well. The severity of PE varies from patient to patient. Patients with PE may present with infertility.
Premature ejaculation in these patients is usually severe enough that patients ejaculate prior to penetration.
Delayed ejaculation, anejaculation, and male anorgasmia:
Ejaculatory dysfunction (EjD) includes a spectrum of disorders in men ranging from delayed ejaculation to a complete inability to ejaculate, anejaculation, and retrograde ejaculation.
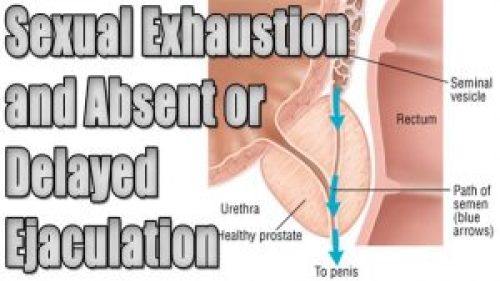
Multiple etiological factors have been identified, including organic and psychogenic factors.
Any medical disease, drug, or surgical procedure that interferes with either central control of ejaculation or the autonomic innervation to the seminal tract can result in delayed ejaculation, anejaculation, and anorgasmia.
Retrograde ejaculation commonly occurs following surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia, whereas anejaculation is always associated with radical prostatectomy or cystoprostatectomy. Orgasm is typically not impaired with these latter procedures.
Lower urinary tract symptoms in aging men are often associated with ejaculatory disorders.
Commonly used drugs such as certain alpha-blockers (eg, tamsulosin ) and antidepressants, particularly serotonin-uptake inhibitors (eg, paroxetine ), have been associated with loss of orgasm or ejaculation.
Loss of ejaculation is often age-related and may be associated with other sexual dysfunction in the male, particularly ED

Read More …
Polycystic ovarian syndrome – not just a gynecological problem
Subacute Thyroiditis
Alprostadil / Caverject injections for erectile dysfunction
Do you feel tired all the time? know the causes
Facial Hair in women
