Dulaglutide is a long-acting GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide 1) agonist that enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion and delays gastric emptying, thus it controls postprandial blood sugars.
Chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension require a timely intake of medications. Diabetes may be controlled with diet and exercise early in its course.
As time progresses blood sugars increase owing to the increase in insulin resistance at the tissue level and decrease in insulin production by the pancreas.
It is estimated that 50% of diabetic patients require insulin after 8 years of their illness.
How is type 2 diabetes managed?
Metformin is the initial drug of choice in type 2 diabetes. Other classes of medicines like DPP-4 (dipeptidyl peptidase 4) inhibitors (Sitagliptin, vildagliptin, saxagliptin, and linagliptin) are added if glycemic goals are not achieved.
Physicians might add a third medicine like sulfonylureas (glimepiride, glyburide, gliclazide) or SGLT-2 (sodium glucose co-transporter 2) inhibitors (dapagliflozin, canagliflozin) or basal insulin at this stage.
Some patients, especially those who have kidney, liver and heart diseases and those who are very lean may be switched directly to insulin at this point.
The role of Insulin
Insulin may be started as a premixed combination of 70% or 75% long-acting and 30% or 25% short or rapid-acting insulin or basal and bolus insulin regimen.
Basal Bolus regimen is using rapid or short-acting insulin prior to every meal and long-acting insulin at bedtime.
This regimen is close to the ideal situation. Except for a minority of patients, almost all patients on Insulin also require oral anti-diabetic medicine as an insulin sensitizer. This makes the regimen more complex.
The most common adverse effects of insulin and sulfonylurea are hypoglycemia and weight gain. Since most of the diabetic patients are overweight or obese, adding insulin or sulfonylurea add to the problem.
Which antidiabetic medicines cause weight loss?
Since most diabetic patients are obese, physicians advise their patients to lose weight. Ten to fifteen kilograms of weight loss has been associated with a marked reduction in insulin requirement.
Along with anti-diabetic diet, weight loss of up to fifteen kilograms has been seen to reverse diabetes in early stages of diabetes. “Reverse diabetes” here only means that the patient is off medications for some time.
Weight loss with low-calorie diet and exercise is one of the pillars of management of diabetes in obese patients. Patients who are on insulin or sulfonylureas tend to gain weight despite intake of low calories and adequate exercise.
Some patients starve but weight loss is minimal, this is where genes play an important role. Nonetheless, with the advent of GLP-1 agonists like liraglutide and the new arrival dulaglutide, there is some hope for obese diabetic patients to lose weight.
Liraglutide and dulaglutide are FDA approved drugs for weight loss. Metformin and DPP-4 inhibitors are said to be weight neutral and sulfonylureas and thiazolidinediones like pioglitazone cause weight gain.
Mechanism of GLP 1 agonists (e.g Dulaglutide)
Glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists include exenatide, liraglutide, and dulaglutide. These drugs cause insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner.
This means that insulin secretion is enhanced when blood sugars rise. Thus these drugs have low potential to cause hypoglycemia.
GLP-1 agonists also delay gastric emptying. This leads to slow absorption of carbohydrates, thus reducing the post-prandial (post meals ) spike in blood sugars after meals.
GLP-1 agonists also inhibit inappropriate secretion of glucagon, a hormone with opposite effects to insulin.
About Dulaglutide (Trulicity)
GLP 1 agonists include exenatide which requires twice-daily administration through a syringe.
Liraglutide, first approved as a weight loss medicine also requires to be injected daily. The new addition to this group is dulaglutide.
Dulaglutide is an ultra-long-acting GLP-1 agonist that requires to be injected weekly. Weekly administration along with properties to reduce weight, improve hyperglycemia and relatively cheaper than its sister drug (liraglutide), makes it a better option for obese diabetic patients.
The dose of dulaglutide:
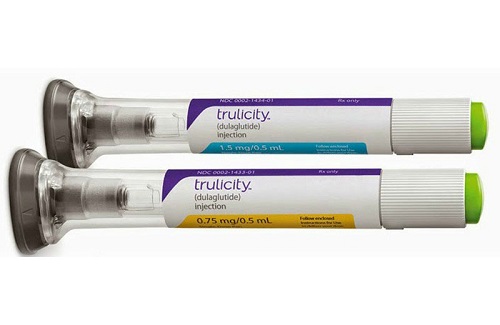
Dulaglutide is available in 0.75mg and 1.5 mg dose throughout the world. In Pakistan, it is to be launched in a fixed dose of 1.5 mg which is to be injected like insulin once weekly.
Administration :
Like insulin, dulaglutide is an injectable drug, given as a weekly subcutaneous injection in the abdomen and upper thighs.
If the dose is missed it can be given within a maximum of three days of the missed dose. If less than three days remain before the next dose is scheduled, the previous dose can be missed.
Cost of Dulaglutide in Pakistan
In Pakistan, dulaglutide will cost about Rs. 14000/- (fourteen thousand) per month.
Contraindications to dulaglutide:
Like other GLP-1 agonists, dulaglutide can cause nausea, vomiting and hypersensitivity reactions.
It has been associated with pancreatitis and should not be given to patients with the previous history of pancreatitis.
It is also contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma.
Dulaglutide / Trulicity side effects:
Since dulaglutide delays gastric emptying, the most frequent adverse effects relate to the gastrointestinal tract.
The patient may notice post-meals bloating, heartburn and flatulence. It can also cause hypoglycemia, especially when added to insulin or sulfonylurea.
Insulin dose may need to be reduced when dulaglutide is added. Although dose adjustment in renal failure is not advised. However, it has been shown in some patients to cause worsening of renal failure.
Dulaglutide should not be used in patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus and patients at risk of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Pregnancy and lactation:
Dulaglutide is not approved for pregnant and lactating patients with diabetes. Pregnant patients using dulaglutide are at risk of developing eclampsia and preeclampsia (complications of hypertension in pregnancy).
Take Appointment for Diabetes here
Read more …
Dapagliflozin launched in Pakistan
Role of Aspirin in the prevention of vascular events
Are statins safe and effective in children